A Comparative Study of Diesel Oil and Soybean Oil as Oil-Based Drilling Mud
Summary
This study evaluates the performance of high oleic soybean oil (HOSO) as a sustainable alternative to diesel oil in oil-based drilling muds, with implications for both lubricant and biodiesel applications. The research compares the rheological, filtration, and thermal properties of drilling fluids formulated with HOSO versus conventional diesel oil.
Full citation: Agwu, O. E., Okon, A. N., & Udoh, F. D. (2015). A comparative study of diesel oil and soybean oil as oil‑based drilling mud. Journal of Petroleum Engineering, 2015, Article 828451. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/828451
Key Findings:
-Rheological Performance: HOSO-based muds exhibit Bingham plastic behavior with lower yield point and gel strength than diesel-based muds, indicating better pumpability and lower energy requirements.
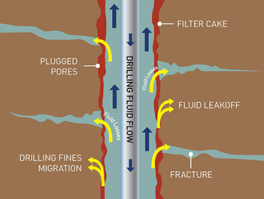
-Filtration Properties: HOSO muds showed lower fluid loss and thinner, softer filter cakes—reducing the risk of stuck pipe incidents during drilling.
-Thermal Stability: HOSO has a significantly higher flash point (330°C vs. 70°C for diesel), making it safer for high-temperature drilling environments.
-Environmental Impact: HOSO is biodegradable, non-toxic, and renewable, offering a safer and more sustainable alternative to petroleum-based fluids.
-Economic Consideration: While historically more expensive, the cost of HOSO has become competitive with diesel, especially when factoring in environmental and safety benefits.
🌱 Relevance to Green Chemistry Educators: This paper is highly relevant for educators teaching green chemistry, sustainability, or environmental engineering:
1. Real-World Application of Green Chemistry Principles
-Use of renewable feedstocks: HOSO is derived from soybeans, a renewable agricultural product.
-Design for energy efficiency: Lower viscosity and gel strength reduce energy consumption during drilling.
-Safer chemicals: HOSO is non-toxic and has a high flash point, reducing fire and health hazards.
2. Interdisciplinary Teaching Tool
-Connects chemistry, environmental science, petroleum engineering, and industrial sustainability.
-Offers a case study for evaluating trade-offs in material selection (performance vs. environmental impact).
3. Supports NGSS and Sustainability Education
-Aligns with NGSS standards related to Earth and human activity, engineering design, and energy.
-Encourages systems thinking and life-cycle analysis in evaluating industrial processes.
4. Promotes Critical Thinking and Innovation
-Students can explore how bio-based materials can replace fossil-derived ones in high-performance applications.
-Encourages discussion on the role of green chemistry in industrial innovation and climate solutions.
Full citation: Agwu, O. E., Okon, A. N., & Udoh, F. D. (2015). A comparative study of diesel oil and soybean oil as oil‑based drilling mud. Journal of Petroleum Engineering, 2015, Article 828451. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/828451
Key Findings:
-Rheological Performance: HOSO-based muds exhibit Bingham plastic behavior with lower yield point and gel strength than diesel-based muds, indicating better pumpability and lower energy requirements.
-Filtration Properties: HOSO muds showed lower fluid loss and thinner, softer filter cakes—reducing the risk of stuck pipe incidents during drilling.
-Thermal Stability: HOSO has a significantly higher flash point (330°C vs. 70°C for diesel), making it safer for high-temperature drilling environments.
-Environmental Impact: HOSO is biodegradable, non-toxic, and renewable, offering a safer and more sustainable alternative to petroleum-based fluids.
-Economic Consideration: While historically more expensive, the cost of HOSO has become competitive with diesel, especially when factoring in environmental and safety benefits.
🌱 Relevance to Green Chemistry Educators: This paper is highly relevant for educators teaching green chemistry, sustainability, or environmental engineering:
1. Real-World Application of Green Chemistry Principles
-Use of renewable feedstocks: HOSO is derived from soybeans, a renewable agricultural product.
-Design for energy efficiency: Lower viscosity and gel strength reduce energy consumption during drilling.
-Safer chemicals: HOSO is non-toxic and has a high flash point, reducing fire and health hazards.
2. Interdisciplinary Teaching Tool
-Connects chemistry, environmental science, petroleum engineering, and industrial sustainability.
-Offers a case study for evaluating trade-offs in material selection (performance vs. environmental impact).
3. Supports NGSS and Sustainability Education
-Aligns with NGSS standards related to Earth and human activity, engineering design, and energy.
-Encourages systems thinking and life-cycle analysis in evaluating industrial processes.
4. Promotes Critical Thinking and Innovation
-Students can explore how bio-based materials can replace fossil-derived ones in high-performance applications.
-Encourages discussion on the role of green chemistry in industrial innovation and climate solutions.
Keyword Tags
